
A new plant-based substitute for polyurethane foam eliminates the health risk of the material, commonly found in insulation, car seats and other types of cushioning, and it’s more environmentally sustainable, our new research shows.
Polyurethane foams are all around you, anywhere a lightweight material is needed for cushioning or structural support. But they’re typically made using chemicals that are suspected carcinogens.
Polyurethanes are typically produced in a very fast reaction between two chemicals made by the petrochemical industry: polyols and isocyanates. While much work has gone into finding replacements for the polyol component of polyurethane foams, the isocyanate component has largely remained, despite its consequences for human health. Bio-based foams can avoid that component.

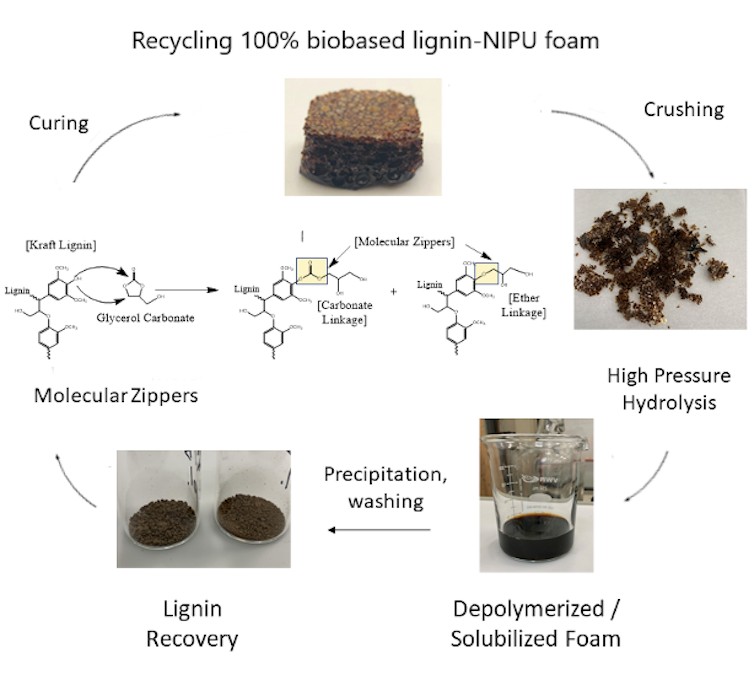
We created a durable bio-based foam using lignin, a byproduct of the paper pulping industry, and a vegetable oil-based curing agent that introduces flexibility and toughness to the final material.
At the heart of the innovation is the ability to create a system that “gels,” both in the sense that the materials are compatible with one another and that they physically create a gel quickly so that the addition of a foaming agent can create the lightweight structure associated with polyurethane foams.
Lignin is a difficult material to convert into a usable chemical, given its complicated and heterogeneous structure. We used this structure to create a network of bonds that enabled what we believe is the world’s first lignin-based nonisocyanate foam.
The foam can also be recycled because it has bonds that can unzip the chemical network after it has formed. The main components used to produce the foam can then be extracted and used again.
Why it matters
Polyurethane foams are the world’s sixth-most-produced plastic yet among the least recycled materials. They are also designed for durability, meaning they will remain in the environment for several generations.
They contribute to the plastic waste problem for the world’s oceans, land and air, and to human health problems. Today, plastics can be found in virtually every creature in the terrestrial ecosystem. And since most plastics are made from petroleum products, they’re connected to fossil fuel extraction, which contributes to climate change.
The fully bio-based origin of our foams addresses the issue of carbon neutrality, and the chemical recycling capability ensures that waste plastic has a value attached to it so it is less likely to be thrown away. Ensuring waste has value is a hallmark of the circular approach to manufacturing – attaching a monetary value to things tends to decrease the amount that is discarded.
We hope the nature of these foams inspires others to design plastics with the full life cycle in mind. Just as plastics need to be designed according to properties of their initial application, they also need to be designed to avoid the final destination of 90% of plastic waste: landfills and the environment.
What’s next
Our initial versions of bio-based foams produce a rigid material suitable for use in foam-core boards used in construction or for insulation in refrigerators. We have also created a lightweight and flexible version that can be used for cushioning and packaging applications. Initial testing of these materials showed good durability in wet conditions, increasing their chance of gaining commercial adoption.

Polyurethane foams are used so extensively because of their versatility. The formulation that we initially discovered is being translated to create a library of precursors that can be mixed to produce the desired properties, like strength and washability, in each application.
Srikanth Pilla is a professor of engineering at Clemson University. James Sternberg is a research assistant professor of automotive engineering at Clemson. This post originally appeared at The Conversation.
Weekly Newsletter
Get building science and energy efficiency advice, plus special offers, in your inbox.









8 Comments
Sounds great if it can scale. For plant-based rigid insulation used in buildings, I'd want to make sure that bugs don't like to eat or burrow in it. Mineral wool has a lot of properties that I like, but if there was a rigid foam that ants didn't burrow in I'd be very interested. Keeping things dry helps with bugs, but ants and increasingly termites make me nervous about using foams for external insulation.
Right on! There are always unintended consequences of new products, and the professionals are left holding the bag when something happens. My daughters Prius had soy base wiring and mice ate it all up and all wiring had to be replaced. I wish i could use foam based insulation, but they are way too toxic with long term off gassing. For now, I recommend use BIB to seal up pretty good + Aeroseal spray. Other ideas?
It would be great to incorporate mineral wool into a plant based foam to add fire resistance and insect resistance to it. Also this article is really missing key info, like R value. C'mon guys how can you advertise your insulation product without letting us know the R value?
richmas62,
They are a group of researchers at a university, not a manufacturer. They aren't advertising a product, they are saying they have figured out how to create a variety of plant based foams from which products may be made.
Are there EPDs available yet? I'd love to see the carbon footprint of this product. Since we use rigid board primarily on the outside of the building, as an architect I am more concerned about the GWP than the carcinogens. But concerned about both.
As Malcolm said in #4, this isn't a product. When they say it's on the horizon, they mean it is far away, but is just beginning to be foreseeable.
right, thanks.
Lignin is a tough nut to crack in terms of just stripping it out of wood fiber so having a ready market for it would be nice. In the meanwhile I just wish we could incentivize a bunch of regional Gutex factories around the US. Gutex already solves these problems and stores way more carbon along the way. Furthermore it would monetize the millions of tons of slash we generate every year and the millions more tons of slash we need to be clearing out of our most fire-prone forests.
Log in or create an account to post a comment.
Sign up Log in