
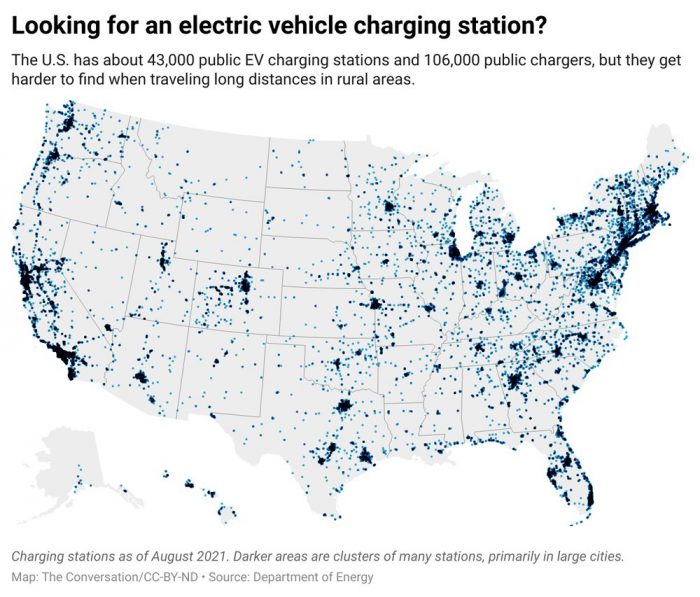
Most of America’s 107,000 gas stations can fill several cars every five or 10 minutes at multiple pumps. Not so for electric vehicle chargers—at least not yet. Today the U.S. has around 43,000 public EV charging stations, with about 106,000 outlets. Each outlet can charge only one vehicle at a time, and even fast-charging outlets take an hour to provide 180 to 240 miles’ worth of charge; most take much longer.
The existing network is acceptable for many purposes. But chargers are very unevenly distributed; almost a third of all outlets are in California. This makes EVs problematic for long trips, like the 550 miles of sparsely populated desert highway between Reno and Salt Lake City. “Range anxiety” about longer trips is one reason electric vehicles still make up fewer than 1% of U.S. passenger cars and trucks.
This uneven, limited charging infrastructure is one major roadblock to rapid electrification of the U.S. vehicle fleet, considered crucial to reducing the greenhouse gas emissions driving climate change.
It’s also a clear example of how climate change is an infrastructure problem–my specialty as a historian of climate science at Stanford University and editor of the book series “Infrastructures.”
Over many decades, the U.S. has built systems of transportation, heating, cooling, manufacturing, and agriculture that rely primarily on fossil fuels. The greenhouse gas emissions those fossil fuels release when burned have raised global temperature by about 1.1°C (2°F), with serious consequences for human lives and livelihoods, as the recent report from the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change demonstrates.
The new assessment, like its predecessor, “Special Report: Global Warming of 1.5°C,”, shows that minimizing future climate change and its most damaging impacts will require transitioning quickly away from fossil fuels and moving instead to renewable, sustainable energy sources such as wind, solar, and tidal power.
That means re-imagining how people use energy: how they travel, what and where they build, how they manufacture goods, and how they grow food.
Gas stations are transport infrastructure, too
Gas-powered vehicles with internal combustion engines have completely dominated American road transportation for 120 years. That’s a long time for path dependence to set in, as America built out a nationwide system to support vehicles powered by fossil fuels.
Gas stations are only the endpoints of that enormous system, which also comprises oil wells, pipelines, tankers, refineries, and tank trucks—an energy production and distribution infrastructure in its own right that also supplies manufacturing, agriculture, heating oil, shipping, air travel, and electric power generation.
Without it, your average gas-powered sedan wouldn’t make it from Reno to Salt Lake City either.
Fossil-fuel combustion in the transport sector is now America’s largest single source of the greenhouse gas emissions causing climate change. Converting to electric vehicles could reduce those emissions quite a bit. A recent life-cycle study found that in the U.S., a 2021 battery EV–charged from today’s power grid–creates only about one-third as much greenhouse gas emissions as a similar 2021 gasoline-powered car. Those emissions will fall even further as more electricity comes from renewable sources.
Despite higher upfront costs, today’s EVs are actually less expensive than gas-powered cars due to their greater energy efficiency and many fewer moving parts. An EV owner can expect to save $6,000 to $10,000 over the car’s lifetime versus a comparable conventional car. Large companies including UPS, FedEx, Amazon, and Walmart are already switching to electric delivery vehicles to save money on fuel and maintenance.
All this will be good news for the climate—but only if the electricity to power EVs comes from low-carbon sources such as solar, tidal, geothermal, and wind. (Nuclear is also low-carbon, but expensive and politically problematic.) Since our current power grid relies on fossil fuels for about 60% of its generating capacity, that’s a tall order.
To achieve maximum climate benefits, the electric grid won’t just have to supply all the cars that once used fossil fuels. Simultaneously, it will also need to meet rising demand from other fossil-fuel switchovers, such as electric water heaters, heat pumps, and stoves, to replace the millions of similar appliances currently fueled by natural gas.
The infrastructure bill
The 2020 Net-Zero America study from Princeton University estimates that engineering, building, and supplying a low-carbon grid that could displace most fossil-fuel uses would require an investment of around $600 billion by 2030.
The infrastructure bill now being debated in Congress was originally designed to get partway to that goal. It initially included $157 billion for EVs and $82 billion for power grid upgrades. In addition, $363 billion in clean energy tax credits would have supported low-carbon electric power sources, along with energy storage to provide backup power during periods of high demand or reduced output from renewables. During negotiations, however, the Senate dropped the clean energy credits altogether and slashed EV funding by over 90%.
Of the $15 billion that remains for electric vehicles, $2.5 billion would purchase electric school buses, while a proposed EV charging network of some 500,000 stations would get $7.5 billion—about half the amount needed, according to Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm.
As for the power grid, the infrastructure bill does include about $27 billion in direct funding and loans to improve grid reliability and climate resilience. It would also create a Grid Development Authority under the U.S. Department of Energy, charged with developing a national grid capable of moving renewable energy throughout the country.
The infrastructure bill may be further modified by the House before it reaches President Joe Biden’s desk, but many of the elements that were dropped have been added to another bill that’s headed for the House: the $3.5 trillion budget plan.
As agreed to by Senate Democrats, that plan incorporates many of the Biden administration’s climate proposals, including tax credits for solar, wind, and electric vehicles; a carbon tax on imports; and requirements for utilities to increase the amount of renewables in their energy mix. Senators can approve the budget by simple majority vote during “reconciliation,” though by then it will almost certainly have been trimmed again.
Overall, the bipartisan infrastructure bill looks like a small but genuine down payment on a more climate-friendly transport sector and electric power grid, all of which will take years to build out.
But to claim global leadership in avoiding the worst potential effects of climate change, the U.S. will need at least the much larger commitment promised in the Democrats’ budget plan.
Like an electric car, that commitment will seem expensive upfront. But as the recent IPCC report reminds us, over the long term, the potential savings from avoided climate risks like droughts, floods, wildfires, deadly heat waves, and sea-level rise would be far, far larger.
Paul N. Edwards is the William J. Perry Fellow in International Security, Center for International Security and Cooperation, Stanford University. This post was originally published at The Conversation.
Weekly Newsletter
Get building science and energy efficiency advice, plus special offers, in your inbox.














5 Comments
From a political perspective, yes, we need to make a fuss about needing a stronger commitment to EV and other clean energy infrastructre.
From the perspective of EV adoption, it's important to also be clear that the infrastructure we have now is fine for most EV owners. Most charging happens at home, and most trips are served well by the DC fast charge (DCFC) stations that are already in operation. Prospective EV purchasers can go to https://abetterrouteplanner.com, put in a trip they would like to be able to do by EV, and get a recommended route including whatever charging stops are needed. Most will find that there are chargers where they need them for their regular trips.
We do need to expand that infrastructure, to better serve areas that are underserved now, to expand capacity as the number of EVs grows, and to get the additional energy needed from clean sources. But people needn't wait for that before buying EVs. You can make the switch now. Bigger sales numbers for EVs will help move manufacturers in that direction and help make the case for rapid expansion of the public charging network.
There is always hydrogen powered vehicles. Time to modernize to support ev and hydrogen.
Paul, I own an EV and I've travelled all over the US with absolutely no trouble at all charging. I have a Tesla. Your article fails to mention the biggest electric vehicle manufacturer in the world even once. They figured out charging infrastructure years ago. In fact, they just completed a factory that can produce 10,000 superchargers per year. https://insideevs.com/news/531709/tesla-completes-supercharger-factory/ They already have over 25,000 of these chargers in operation. I have only had to wait for one once in the last year, and I waited less than 5 minutes. I understand that other auto manufacturers have failed to build charging infrastructure, and that is a problem that needs to be addressed. However, I think you do a disservice to electric vehicles by failing to mention that the largest EV manufacturer in the world has already figured this out.
Matteus, you'll be pleased to know that there are now even more CCS charging locations than Tesla Supercharger locations in the US. Tesla led that way but people should not feel they have to buy a Tesla to be able to charge on the road now.
Also, the opening paragraph is either misleading or out of date: "and even fast-charging outlets take an hour to provide 180-240 miles’ worth of charge; most take much longer."
That's not true. I own a Tesla and just this last weekend added 150 miles of range in 15 minutes. Here's an article from a few months ago breaking down the charging time of a Tesla Model 3 using a fast charger: https://insideevs.com/news/506520/tesla-model-3-supercharger-test/
Log in or create an account to post a comment.
Sign up Log in