HERS Report question
Energy Star Reports show an estimate of Loads for “AS Designed” and Energy Star
The units are Normalized,Modified End Use Loads (MMbtu’s/year)
What is the definition of Normalized, Modified End Use?
How does that compare to what is read at the meter?
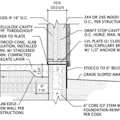
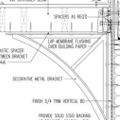
GBA Detail Library
A collection of one thousand construction details organized by climate and house part






Replies
John,
For what it's worth — and I must admit that this paragraph is not a sterling example of clear technical writing — here is a published explanation of "modified end-use loads":
"The new HERS council rating method uses the Modified End-Use Load method. The loads are modified by applying a ratio of the efficiency in the building to the minimum efficiency specified by the HERS Guidelines as a function of system type and fuel type. If two or more systems are present in a building, each portion of the load is applied to its own specific ratio. You can think of it as the same method, but having one end-use per fuel type. For example: If you specify a gas fired air distribution system servicing 60% of the heating load, and electric resistance for the remaining 40% of the heating load then 60% of the heating load is applied to the ratio of (specified gas AFUE to HERS Reference AFUE (78 AFUE)), and the remaining 40% of the load is applied to the ratio of (efficiency of the specified electric resistance (100%) to the HERS Reference efficiency) (which is an HSPF of 6.8, as the HERS reference mandates a conversion to an air-source heat pump)."
The explanation comes from this document:
http://www.archenergy.com/products/rem/rem_rate//ratefaq.pdf
"Normalization" of energy data usually refers to weather normalization — in other words, applying corrective factors to real-world data to account for deviations of weather during the monitoring period from "normal" anticipated weather.