
When you first start learning building science, you may run into this thing called exfiltration. It’s not a widely used word, even among those of us who work in the world of building science. We learn about it and then mostly don’t use it. So why learn about it at all? Is it important?
What is exfiltration?
Air is a wonderful thing, but it can be hard to grasp. Just try. Grab a handful, close your fingers around it, and it’s gone. Its behavior in buildings is our main interest here, and there a few basic rules. The one that matters most to this discussion is that the air leaking into a house will be matched by an equal amount of air leaking out.
We call the air leaking into the house infiltration, and the air that leaks out is exfiltration. Makes perfect sense, right? You may have felt both sides of this air leakage without realizing the difference. In an old house, for example, you can stand next to a leaky door or window and feel a cold draft in winter as infiltration brings that cold outdoor air inside. The most dramatic example of exfiltration is that whoosh of warm air you feel when you go up the attic stairs on a cold day and then look down into the house from above.
The stack effect and exfiltration
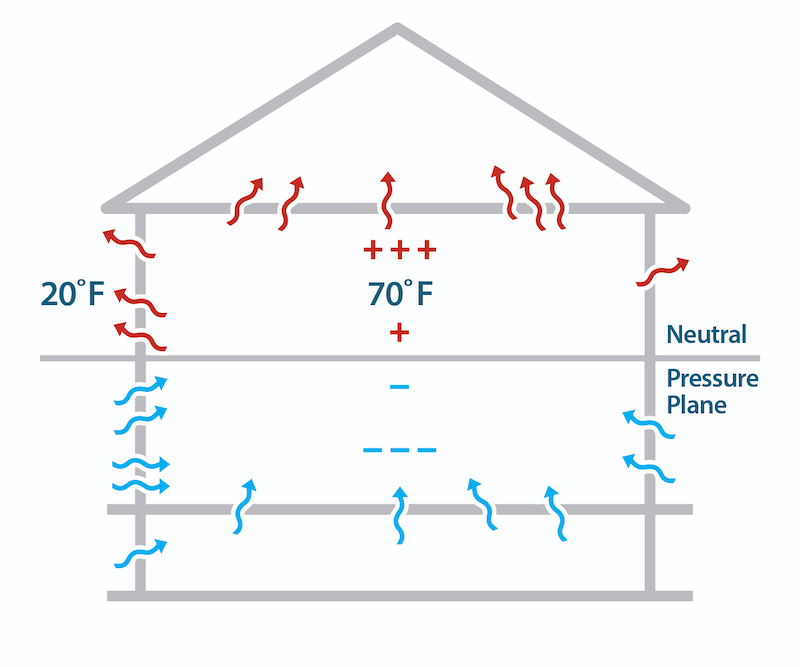
One place where it makes a lot of sense to talk about exfiltration is with the stack effect. Warm air rises in a house. If there are air leakage pathways in the building enclosure, air leaks in below the neutral pressure plane and out above the neutral pressure plane. So, we get infiltration below the neutral pressure plane and exfiltration above it.
More about exfiltration
One of the other rules of air leakage is that air moves from high pressure to low pressure. Exfiltration means air is moving from inside to outside, so the part of the house that’s exfiltrating is at a higher pressure than the air on the other side of the floor, wall, or ceiling that it moves through.
Those positive pressure areas can arise from more than just the stack effect. Just closing a door can create a positive pressure in a bedroom if there’s not an adequate return air pathway. The condo I used to live in would develop a significant positive pressure in one bedroom with the door closed and air handler running. The air being pumped in there had to go somewhere, so a good amount of it exfiltrated.
![Wind creates positive and negative pressures, which result in infiltration and exfiltration [Image courtesy of The Energy Conservatory]](https://www.energyvanguard.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/wind-pressure-positive-negative-800.jpg)
Does this even matter?
The way we talk about building science phenomena does matter. If you call Tyvek Home Wrap a vapor barrier—and some do—you’re not only incorrect, but you confuse other people. If you refer to all air leakage as infiltration—and I’ve heard this, too—you’re also giving others bad information. The total air leakage in a house is a combination of infiltration and exfiltration.
It also matters because infiltration and exfiltration have different effects. Infiltration can bring in unconditioned air, humidity, and pollutants. Exfiltration sends conditioned air and moisture out of the house. Both flows often travel through interstitial spaces, though, and can cause problems along the way. If you have a building cavity with a sweating supply duct in summer, for instance, infiltration may be the problem. Exfiltration of indoor air into a wall cavity can cause moisture problems on exterior sheathing.
All this is really important when you’re trying to solve building performance problems. When we do consulting jobs, we often have examine which way the air is flowing so we can figure out if that could be the source of the problem. If you’ve heard Dr. Joe Lstiburek speak, you may have heard the story of how he proved that the U.S. Congress sucks. He went into one of the tunnels beneath the complex and found a huge rush of airflow toward the Capitol.
In short, the total amount of air leakage is important, but so is the direction of that airflow.
________________________________________________________________________
Allison A. Bailes III, PhD is a speaker, writer, building science consultant, and the founder of Energy Vanguard in Decatur, Georgia. He has a doctorate in physics and writes the Energy Vanguard Blog. He also has written a book on building science. You can follow him on Twitter at @EnergyVanguard. Images courtesy of author, except where noted.
Weekly Newsletter
Get building science and energy efficiency advice, plus special offers, in your inbox.















One Comment
Exfiltration In relation to an ERV installation in a 2 story house -
Conventional wisdom is supply air to the bedrooms (upstairs). However, if we think the stack effect is already exerting pressure upstairs to force air out through the walls, when a bedroom door is closed will we be adding to the pressure in the room causing more exfiltration? I know the door should be undercut (3/4"?), but is this supply air possibly adding to the problem? Maybe some supply and some exhaust?
Log in or create an account to post a comment.
Sign up Log in